Agentic Process Automation represents a new and novel approach to automation that involves the use of AI Agents to automate processes, employing LLMs to enhance decision-making and execution capabilities.
In this article, we will dive into the possible future with APA – the evolution from RPA to APA, delve into the mechanics of agentic workflows, examine the role of AI agents in automation, compare APA with RPA, discuss the benefits and challenges of APA, and look ahead to the future of automation.
Let’s get started!
What is Agentic Process Automation (APA)
APA leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to automate complex, dynamic workflows. It autonomously constructs, executes, and adapts workflows with minimal people intervention.
Unlike traditional Robotic Process Automation (RPA), which relies on rule-based systems, APA leverages the power of Large Language Models (LLMs) to automate complex workflows dynamically and intelligently. This new approach represents a significant leap forward in automation technology, offering unprecedented flexibility, adaptability, and efficiency.
The Evolution of Digital Automation
Digital Automation has undergone a significant transformation over the years, evolving from basic rule-based systems to sophisticated AI-driven processes. Every stage signifies significant technological progress and business influence, showcasing the ongoing incorporation of AI – from rule-based to machine learning, Generative AI, and now AI Agents – all aimed at improving operational efficiency and decision-making abilities.
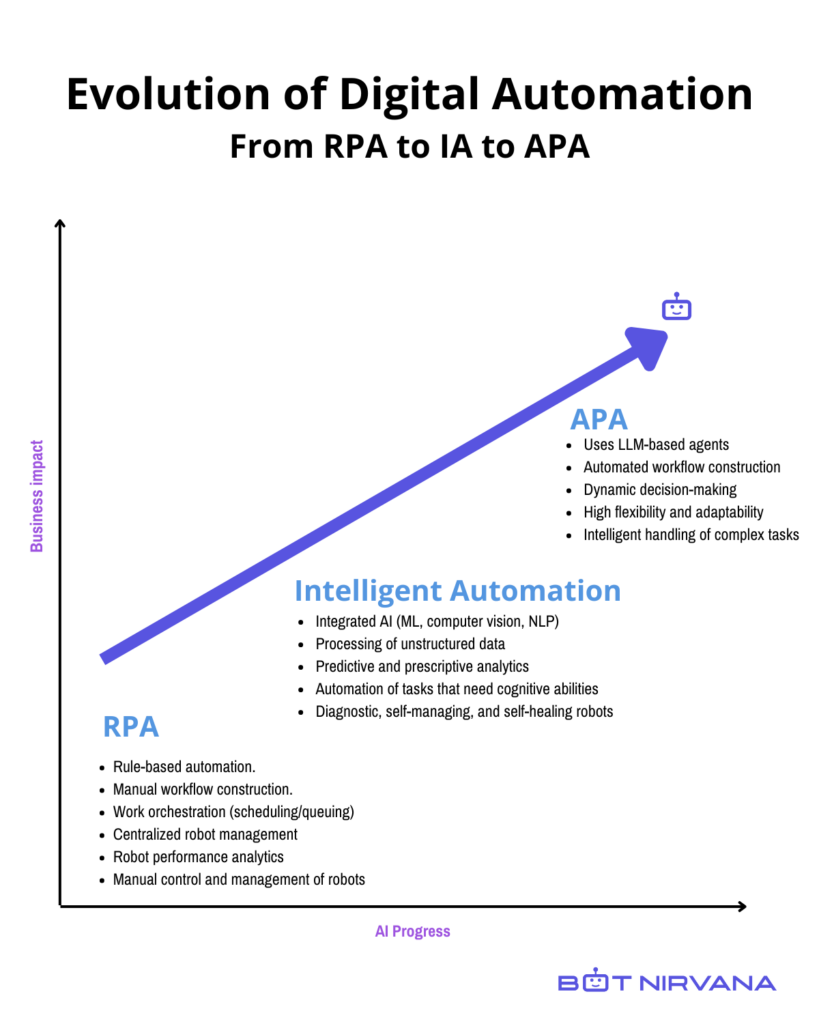
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
The first phase in the evolution of digital automation started with Robotic Process Automation (RPA). RPA involves the use of software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks that are typically performed by humans. RPA relies heavily on predefined rules and scripts, making it suitable for tasks that follow a clear, unchanging set of instructions. Key characteristics of RPA include manual workflow construction, centralized robot management, and the need for people to manage and control robots. RPA’s primary benefits are cost reduction, increased speed, and improved accuracy in performing routine tasks. However, its limitations become evident when dealing with unstructured data or tasks requiring cognitive abilities, as it lacks the flexibility and adaptability needed for more complex processes.
Intelligent Automation (IA)
The second phase, Intelligent Automation (IA), builds on the foundations of RPA by integrating advanced AI technologies such as machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision. IA enhances the capabilities of automation systems by enabling them to process unstructured data, perform predictive and prescriptive analytics, and automate tasks that require cognitive abilities. This phase also introduced diagnostic, self-managing, and self-healing robots, which can identify and resolve issues. Intelligent Automation allows for more sophisticated automation solutions that can adapt to changing conditions and make informed decisions based on data analysis. As a result, IA offers greater business impact by improving efficiency, accuracy, and overall operational performance.
Agentic Process Automation (APA)
The third and current phase in the evolution of automation is with AI Agents and what is being termed Agentic Process Automation (APA). APA represents a significant leap forward by leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI agents to create autonomous, intelligent systems capable of dynamically constructing and executing workflows. Unlike RPA and IA, which rely on predefined rules and human oversight, APA enables AI agents to interpret tasks, make real-time decisions, and continuously adapt workflows based on real-time data. This phase offers high flexibility and adaptability, allowing automation systems to handle complex and dynamic tasks intelligently. APA’s ability to autonomously create your automation workflows and continuously improve based on feedback sets it apart as the most sophisticated form of digital automation so far.
This evolution from RPA to APA marks a shift from static, predefined automation to a more dynamic, intelligent form of automation that can handle complex tasks.
Understanding AI Agents And Agentic Workflows
At the heart of APA lies the concept of AI Agents and Agentic workflows. Unlike traditional workflows that are rigid and rule-based, agentic workflows are designed to be flexible, adaptive, and capable of real-time decision-making. In an agentic workflow, AI agents act autonomously to achieve predefined goals set by human users. These agents can plan, integrate with various tools, and act while continuously refining and adapting.
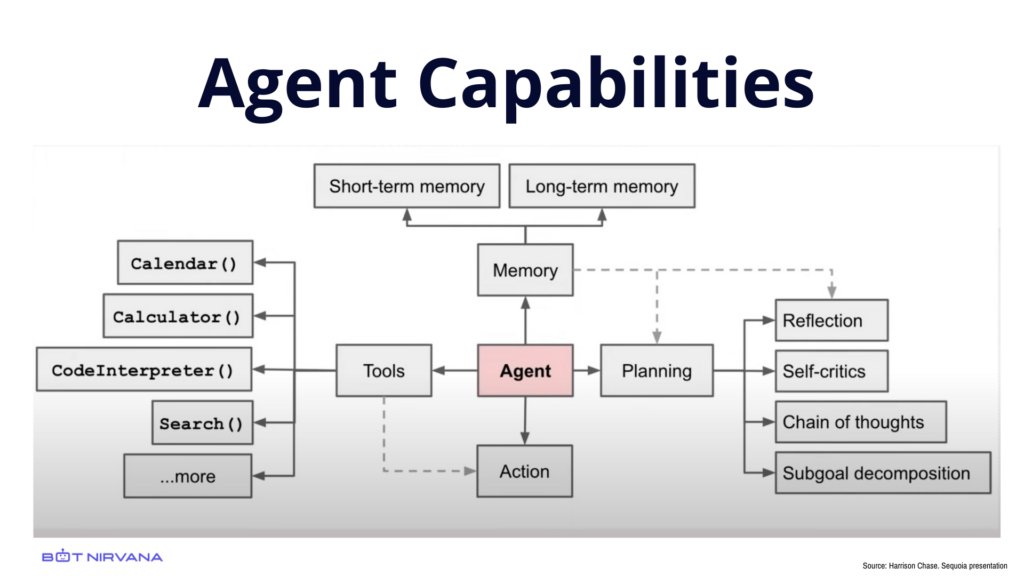
The key to agentic workflows is their ability to operate independently, make decisions, and take actions without much human oversight. This autonomy is made possible by the advanced capabilities of LLMs, which can understand and reason through complex scenarios, and learn from experience to improve over time.
How APA Works – The Role of AI Agents in Automation
AI agents are the driving force behind APA. These agents leverage the power of LLMs to perform a wide range of functions that traditionally require your intervention. Here’s a conceptual overview of how APA works based on the paper “ProAgent: From Robotic Process Automation to Agentic Process Automation”, detailing the key steps involved in its implementation:
- Task Interpretation:
The process begins with AI agents interpreting user instructions. These instructions can be provided in natural language, making it easier for non-technical users to define what needs to be done. The agents use advanced language models to understand the tasks, breaking them down into actionable components.
- Workflow Construction:
Once the tasks are interpreted, the AI agents constructs the workflows required to execute them. This construction can be achieved through various methods, one approach detailed in the paper is the use of JSON for data flow and Python for control flow. The AI agents automatically design the workflow, ensuring it is robust, efficient, and capable of handling specified tasks.
- Tool Integration:
APA involves seamless integration with existing tools and platforms. Whether it’s connecting to existing APIs or other tools, AI agents integrate the necessary tools into the workflows as needed. This integration is crucial for the execution of tasks and the flow of information.
- Control Logic Management:
A key aspect of APA is its ability to manage control logic dynamically. AI agents utilize the capabilities of LLMs to make real-time decisions during workflow execution. This involves adjusting the workflow based on current conditions, ensuring optimal performance, and handling exceptions effectively.
- Data Processing:
Data plays a critical role in APA. AI agents are equipped to process and analyze data in real-time, extracting valuable insights and making informed decisions. This data-driven approach enhances the accuracy and relevance of the workflows, ensuring that they are always aligned with the latest information.
- Self-Improvement:
A defining feature of APA is its capability for self-improvement. AI agents continuously monitor their performance, reviewing completed workflows and identifying areas for enhancement. This iterative learning process enables APA systems to become more efficient and effective over time, adapting to new challenges and optimizing operations.
So as you can see, APA works by leveraging the advanced capabilities of AI agents to interpret tasks, construct dynamic workflows, integrate seamlessly with tools, manage control logic, process data, execute tasks efficiently, and continuously improve. This holistic approach allows organizations to automate complex processes with the least effort, achieving higher levels of flexibility, accuracy, and operational efficiency. How does this differ from RPA?
APA vs. RPA
APA and RPA represent two distinct approaches to automating business processes, each with its own set of characteristics and capabilities. Here is a summary of the key differences between APA and RPA:
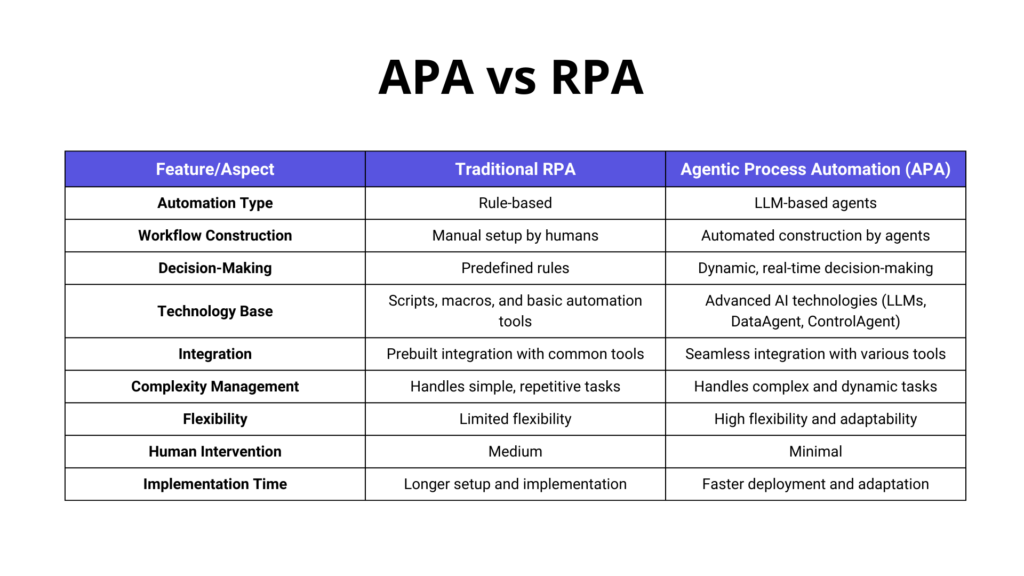
Agentic Process Automation (APA) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) differ significantly in their approaches to automation. RPA is rule-based, relying on predefined scripts and macros to perform tasks, making it suitable for simple, repetitive tasks but limited in handling complex processes. In contrast, APA utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI agents, enabling autonomous workflow creation and real-time decision-making.
RPA’s technology base is centered on pre-built automation actions, whereas APA incorporates advanced AI technologies like DataAgent and ControlAgent, offering a more powerful framework. Integration is another area where APA excels; RPA typically includes prebuilt integrations but lacks adaptability, whereas APA seamlessly integrates with a wide variety of tools. In terms of complexity management, RPA requires quite a bit of effort for setup and maintenance. APA, however, is designed to handle dynamic tasks, significantly reducing the need for human involvement and enhancing operational efficiency.
APA provides high flexibility by continuously adjusting workflows based on real-time data and evolving conditions, unlike RPA’s limited flexibility. Implementation time for RPA is generally longer due to the manual construction of workflows, whereas APA allows for faster deployment and adaptation as AI agents automate the creation and adjustment of workflows.
In summary, while RPA offers effective automation for simple, repetitive tasks, APA significantly enhances automation capabilities by introducing AI-driven, dynamic, and adaptable processes.
Benefits of Agentic Process Automation
Agentic Process Automation (APA) offers a transformative approach to business automation by leveraging advanced AI capabilities. This approach provides several significant benefits that go beyond traditional automation methods.
- Enhanced Efficiency: APA dramatically improves operational efficiency by automating complex and dynamic workflows that were previously too challenging for traditional automation systems. AI agents handle tasks autonomously, reducing the need for human intervention and allowing employees to focus on core activities.
- Greater Flexibility: One of the standout features of APA is its high flexibility and adaptability. Unlike rule-based systems that require manual adjustments, APA uses AI agents capable of real-time decision-making. This adaptability ensures that the automated processes remain effective even as conditions change, maintaining optimal performance without constant human oversight.
- Cost Reduction: By minimizing the need for people to program your workflows and by reducing errors, APA helps organizations save on operational costs. The automation of complex workflows also means that tasks can be completed faster and more accurately, leading to significant cost savings.
- Continuous Improvement: A defining feature of APA is its capability for self-improvement. AI agents continuously learn from their interactions and outcomes, refining their processes and decision-making abilities over time. This iterative learning ensures that the system evolves and improves, becoming more effective with each cycle.
- Seamless Integration: APA offers seamless integration with a wide range of tools and platforms, from enterprise software to communication tools. This integration capability ensures that APA can be incorporated into existing IT infrastructure with minimal disruption, enhancing its utility and effectiveness across different business environments.
- Faster Implementation: Compared to traditional RPA, which often requires lengthy setup and manual configuration, APA allows for quicker deployment. Thanks to automated workflow construction and dynamic adaptability, businesses can implement APA more swiftly and accelerate their return on investment.
Agentic Process Automation represents a significant advancement in the field of digital automation, offering enhanced efficiency, flexibility, and accuracy. Its ability to integrate seamlessly with existing systems, continuously improve, and handle complex decision-making makes it an invaluable tool for modern businesses looking to stay competitive in an increasingly automated world.
While Agentic Process Automation (APA) offers numerous benefits, its implementation and maintenance present several challenges.
Challenges and Solutions
There are many challenges concerning APA. Addressing these challenges effectively is crucial for harnessing the full potential of APA.
- Reliable and Safe Decision-Making: Ensuring the accuracy and safety of decisions made by LLM-based agents is critical. The dynamic nature of APA means that AI agents are making real-time decisions that can significantly impact business operations. To address this challenge, rigorous testing and continuous monitoring of APA systems are essential. Implementing fail-safes and fallback mechanisms can handle errors gracefully. Additionally, making decision-making processes transparent and interpretable facilitates oversight, ensuring that stakeholders can understand and trust the actions taken by AI agents.
- Maintaining Human Control: Maintaining an appropriate level of human control is crucial to prevent over-reliance on automated systems. Clear protocols for human oversight, intervention, and validation of actions taken by APA systems need to be established. By defining specific points where human operators review and validate APA actions, organizations can ensure that critical decisions are cross-checked by human judgment. Training personnel to effectively monitor and manage APA operations is also vital to maintaining a balance between automation and human oversight.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Seamlessly incorporating APA into current IT infrastructure can be challenging, especially for organizations with complex or legacy systems. Developing proven integration strategies that prioritize compatibility and minimal disruption is essential. A modular and scalable approach can gradually incorporate APA into existing workflows, allowing for smooth transitions without major operational disruptions. Collaboration between IT and automation teams can also ensure that APA systems are well-integrated and supported within the broader technological ecosystem.
- Automation Bias: Over-reliance on automated systems can lead to automation bias, where users blindly trust the outputs of AI agents. This can result in overlooking potential errors or biases within the automated processes. To mitigate this risk, it is important to implement robust validation and monitoring mechanisms. Regular audits of APA outputs and decisions can help identify and correct biases. Fostering a culture of critical evaluation among users, where they are encouraged to question and validate automated decisions, can also help prevent blind trust in automation.
- Data Privacy and Security: Handling large volumes of data, including sensitive information, poses significant privacy and security challenges. Ensuring that APA systems comply with data protection regulations and implementing strong security measures is essential to protect against data breaches and unauthorized access. Encryption, access controls, and regular security audits can enhance data security. Additionally, establishing clear data governance policies can help manage and protect data effectively within APA systems.
- Skill Development and Training: Implementing APA requires a workforce skilled in AI Agents, LLMs, and advanced automation technologies. Organizations may face challenges in finding and training personnel with the necessary expertise. Investing in training programs and continuous learning opportunities for employees can help bridge the skill gap.
While the implementation of Agentic Process Automation presents challenges, addressing these through rigorous testing, continuous monitoring, clear protocols, robust integration strategies, and ongoing training can ensure the successful deployment and operation of APA systems. If we do so, APA can emerge as the future of Digital Automation. .
The Future of Digital Automation
The landscape of digital automation is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI). Agentic Process Automation (APA) is at the forefront of this evolution, promising to revolutionize how businesses operate. As we look ahead, several trends and developments are expected to shape the future of digital automation.
Increased Adoption of Agentic AI and APA
As the benefits of APA become more apparent, its adoption is likely to accelerate across various industries. Businesses are recognizing that traditional automation methods, while effective for simple tasks, fall short when it comes to handling complex and dynamic processes. APA’s ability to autonomously manage intricate workflows, make real-time decisions, and continuously improve will drive its widespread adoption. Companies that embrace APA will gain a competitive edge through enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and improved operational accuracy.
Human-AI Collaboration
While APA aims to reduce the need for human intervention in routine tasks, the future will emphasize a symbiotic relationship between humans and AI. This collaboration will leverage the strengths of both, with AI handling data-intensive, repetitive tasks and humans focusing on strategic, creative, and interpersonal activities. AI will augment human capabilities, providing insights and recommendations that aid decision-making. This partnership will not only enhance productivity but also ensure that automation serves to amplify human potential rather than replace it.
Ethical and Safety Standards
As APA systems become more prevalent, there will be a greater focus on establishing ethical and safety standards. Ensuring that AI agents operate transparently and make decisions that align with ethical guidelines will be crucial. Addressing concerns such as automation bias, data privacy, and security will require robust frameworks and regulations. Organizations will need to implement comprehensive oversight mechanisms to monitor AI behavior and outcomes, ensuring that automation technologies are used responsibly and ethically.
Continuous Innovation
The field of digital automation will continue to evolve, driven by ongoing research and development. Advances in AI will lead to the creation of even more sophisticated AI agents capable of handling increasingly complex tasks. Businesses will need to stay abreast of these developments, continuously updating their automation strategies to leverage the latest technologies.
Conclusion
The future of digital automation, led by AI Agents, holds immense promise. As businesses embrace APA and integrate it with other emerging technologies, they will unlock new levels of efficiency, flexibility, and innovation. The focus on human-AI collaboration, ethical standards, and continuous improvement will ensure that automation technologies are used responsibly and effectively. By staying ahead of the curve and adapting to these advancements, organizations can position themselves for success in an increasingly automated world.

Are there any true agentic process automation solutions out there? There’s lot’s of talk of AI agents (AI-powered RPA or intelligent automation), but are there any APA solutions – according to the definition above?
This is a concept at this point based on paper published.
This is no more a concept. it’s become a reality now.
We are building something similar at SyncIQ.ai … Would love to chat if interested.
Awesome. Good luck!
Pingback: Agentic AI: Redefining Automation with Autonomous AI