As we navigate through 2024, artificial intelligence (AI) continues to reshape the business landscape at an unprecedented pace. From customer service to complex business process automation, AI applications are becoming increasingly sophisticated and ubiquitous. Understanding the spectrum of AI tools available is crucial for businesses looking to stay competitive and innovative.
This article will guide you through the AI spectrum, from simple chatbots to advanced AI agent automation. We’ll explore four key Type of AI applications that every business leader should be familiar with in 2024: Chatbots, CoPilots, Domain-Specific AI Agents, and AI Automation (DPA/RPA). Each of these categories represents a different level of AI sophistication and addresses specific business needs.
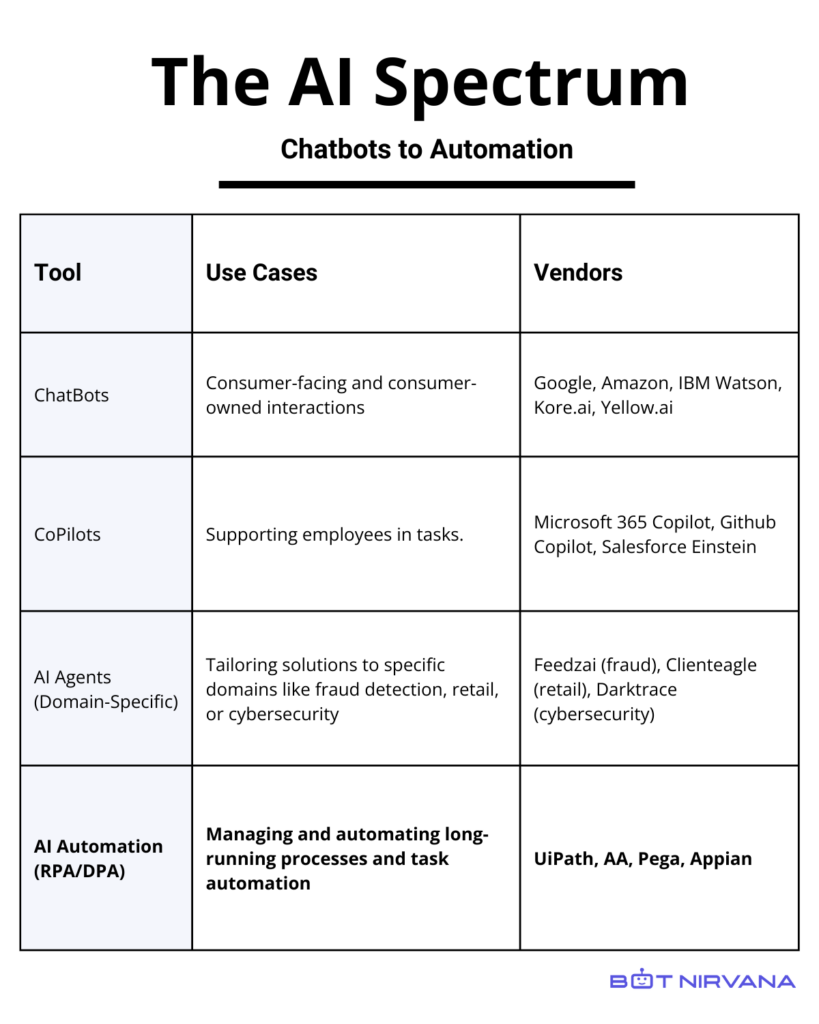
The AI Spectrum: An Overview of Type of AI Applications
The AI spectrum represents a range of type of AI applications, from Chatbots to highly complex, adaptive AI agents. This progression reflects not only increasing technological sophistication but also a shift from general-purpose AI to highly specialized applications. As we move across the spectrum, we see AI tools becoming more targeted, more capable, and more deeply integrated into core business operations.
Chatbots: The Front Line of AI Interaction and Top AI Apps
Chatbots are AI-powered conversational interfaces designed to simulate human-like interactions through text or voice. They use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms to understand user queries and provide appropriate responses.
Key Characteristics:
- 24/7 Availability: Chatbots can operate round the clock, providing instant responses.
- Scalability: They can handle multiple conversations simultaneously.
- Consistency: Chatbots deliver consistent responses for similar queries.
- Multi-lingual Support: Advanced chatbots can communicate in multiple languages.
- Integration Capabilities: They can be integrated with various platforms and backend systems.
Common Use Cases:
- Customer Support: Answering FAQs, troubleshooting common issues, and guiding users through processes.
- E-commerce: Assisting with product recommendations, order tracking, and basic transactions.
- Lead Generation: Qualifying leads by gathering initial information from potential customers.
- Appointment Scheduling: Helping users book appointments or make reservations.
- Information Dissemination: Providing updates on news, weather, or company information.
Sample Vendors and Tools:
- Google (Dialogflow): Offers a comprehensive platform for building conversational interfaces.
- Amazon (Lex): Provides tools for creating chatbots with automatic speech recognition and natural language understanding.
- Kore.ai: Specializes in enterprise-grade conversational AI platforms.
- Yellow.ai: Offers a conversational CX automation platform for various industries.
- Rasa: An open-source framework for building custom, AI-powered chatbots with deep NLP capabilities.
- IBM Watson Assistant: A versatile chatbot platform offering AI-driven conversational interfaces for various industries and use cases.
CoPilots: AI-Powered Employee Assistance and Machine Learning
AI copilots are advanced AI-powered tools designed to assist and augment human tasks across various domains. They work alongside humans, providing real-time suggestions, automating repetitive tasks, and helping with decision-making processes. These copilots leverage large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4, machine learning algorithms, and other AI technologies to understand context, generate content, offer insights, and even interact with other software.
Key Characteristics:
- Contextual Understanding: AI copilots understand the context of a task or conversation, enabling them to provide relevant assistance or generate appropriate content.
- Real-time Assistance: They operate in real-time, offering suggestions, auto-completing tasks, or generating responses as needed.
- Automation of Tasks: They can automate certain tasks directly from the application, allowing users to focus on their current activities.
- Integration with Tools: AI copilots are often integrated into software platforms like IDEs (Integrated Development Environments), document editors, CRM systems, and other business tools to assist users directly within their workflow.
- Learning and Adaptation: They learn from user interactions, improving their performance and recommendations over time.
Common Use Cases:
- Coding Assistance: Tools like GitHub Copilot help developers by suggesting code snippets, completing code, and even writing entire functions based on natural language prompts.
- Writing and Content Creation: AI copilots can help generate articles, social media posts, emails, and more by understanding the context and desired tone.
- Customer Support: AI copilots assist customer service agents by suggesting responses, summarizing customer issues, and automating routine interactions.
- Data Analysis: They can help analyze data, generate reports, and provide insights, making data-driven decision-making more accessible.
- Personal Assistance: AI copilots can manage schedules, set reminders, and perform other administrative tasks, acting like virtual assistants.
Sample Vendors and Tools:
- Microsoft (Copilot for Office 365): Integrates with Microsoft Office apps like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint, providing AI-driven suggestions, automations, and data insights directly within these tools.
- GitHub (Copilot): An AI-powered coding assistant integrated into IDEs like Visual Studio Code, offering code suggestions, completions, and even generating code based on natural language prompts.
- Google (Duet AI): Embedded within Google Workspace, Duet AI offers smart suggestions, content generation, and automation for Google Docs, Sheets, and other apps, streamlining productivity tasks.
- Salesforce (Einstein Copilot): Provides AI-driven insights, recommendations, and automation within the Salesforce CRM platform, enhancing customer relationship management and sales processes.
- Adobe (Firefly): AI-powered creative tools that assist in generating images, editing content, and enhancing creative workflows across Adobe’s suite of design and media applications.
In essence, AI copilots act as intelligent partners in various workflows, enhancing productivity and enabling users to achieve more with less effort.
Domain-Specific AI Agents: Tailored Intelligence and Personalization
Domain-specific AI agents are specialized artificial intelligence systems designed to perform tasks and solve problems within a particular field or industry. These agents leverage deep learning, expert systems, and other AI technologies to provide highly accurate and context-aware solutions for specific domains.
Key Characteristics:
- Specialized Knowledge: Deep understanding of industry-specific terminology, regulations, and best practices.
- High Accuracy: Tailored algorithms that provide more precise results for domain-specific tasks.
- Contextual Awareness: Ability to interpret and respond to industry-specific contexts and nuances.
- Continuous Learning: Capability to learn from new data and experiences within the domain.
- Integration with Domain-Specific Tools: Seamless interaction with industry-standard software and databases.
Common Use Cases:
- Healthcare: Diagnostic assistance, medical image analysis, and drug discovery.
- Finance: Fraud detection, risk assessment, and algorithmic trading.
- Retail: Inventory optimization, demand forecasting, and personalized recommendations.
- Cybersecurity: Threat detection, network anomaly identification, and automated incident response.
- Legal: Contract analysis, legal research assistance, and case outcome prediction.
Sample Vendors and Tools:
- Feedzai: Specializes in AI-powered fraud detection and anti-money laundering for financial institutions.
- Clienteagle: Offers AI solutions tailored for retail operations and customer insights.
- Darktrace: Provides AI-driven cybersecurity platforms for autonomous threat detection and response.
- IBM Watson Health: Offers AI solutions for various healthcare applications, including clinical decision support and drug discovery.
AI Automation (DPA/RPA): Streamlining Business Processes
AI Automation, encompassing Digital Process Automation (DPA) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA), refers to the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies to automate complex, multi-step business processes. These systems can handle end-to-end workflows, make decisions based on predefined rules and AI-driven insights, and interact with multiple applications and data sources.
Key Characteristics:
- End-to-End Process Automation: Capability to automate workflows across different systems and departments.
- Intelligent Decision-Making: Utilization of AI and machine learning for complex decision-making within processes.
- Adaptability: Ability to handle exceptions and adapt to changing conditions or rules.
- Scalability: Can be scaled to handle increased workloads or expanded to new processes.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless interaction with various enterprise systems and databases.
Common Use Cases:
- Finance and Accounting: Invoice processing, account reconciliation, and financial reporting.
- Human Resources: Employee onboarding, payroll processing, and leave management.
- Supply Chain Management: Order processing, inventory management, and logistics optimization.
- Customer Service: Automated ticket routing, customer data updates, and service request processing.
- IT Operations: System monitoring, automated troubleshooting, and software deployment.
Key Vendors and Tools:
- Pega: Offers a comprehensive digital transformation platform with powerful process automation capabilities.
- Appian: Provides a low-code automation platform for building enterprise applications and workflows.
- UiPath: Specializes in RPA solutions for various industries and business functions.
- Automation Anywhere (AA): Offers a range of intelligent automation tools, including RPA and AI-powered bots.
The Interconnected Nature of AI Tools and Applications of Artificial Intelligence
While we’ve discussed these AI applications as distinct categories, in practice, they often work together synergistically. For example, a chatbot might handle initial customer inquiries, but seamlessly hand off complex issues to a human agent supported by a CoPilot. Similarly, domain-specific AI agents might feed into broader process automation systems, creating a comprehensive AI ecosystem.
As AI technologies continue to advance, we’re seeing increasing integration between different types of AI applications. This evolution is leading to more holistic AI solutions that can address multiple business needs simultaneously, creating a more cohesive and intelligent business environment.
Choosing the Right AI Solutions for Your Business: Developing a Successful AI Strategy
When considering AI solutions, it’s crucial to start with a clear understanding of your business objectives. Are you looking to improve customer service, boost employee productivity, enhance decision-making, or streamline operations? Your specific goals will guide you toward the most appropriate AI applications.
Considering the AI Spectrum When Making Decisions
The AI spectrum we’ve discussed provides a useful framework for decision-making. Consider where your needs fall on this spectrum. Do you require simple, customer-facing interactions (chatbots), internal productivity tools (CoPilots), specialized industry solutions (domain-specific agents), or comprehensive process automation (DPA/RPA)?
The Importance of Vendor Selection in AI Strategy
Choosing the right vendor is crucial. Consider factors such as the vendor’s expertise in your industry, their track record of successful implementations, the scalability of their solutions, and their approach to data security and privacy.
Conclusion: Embracing type of AI Applications for Business Success
The AI spectrum, from chatbots to AI agent automation, offers a range of powerful tools for businesses. By understanding these different type of AI applications and how they fit into the broader AI landscape, businesses can make informed decisions about which solutions best meet their needs.
As AI continues to evolve, businesses must stay informed and open to the possibilities these technologies offer. Whether you’re just starting your AI journey or looking to expand your existing capabilities, there’s never been a better time to explore the transformative potential of AI for your business.