The latest Gartner Magic Quadrant for Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has been released, offering a comprehensive view of the rapidly evolving automation market. This year’s report reveals both stability among top players and significant shifts driven by artificial intelligence (AI) advancements. Let’s dive into the key takeaways and what they mean for organizations navigating the complex world of automation.
Stability at the Top, with Notable Movement
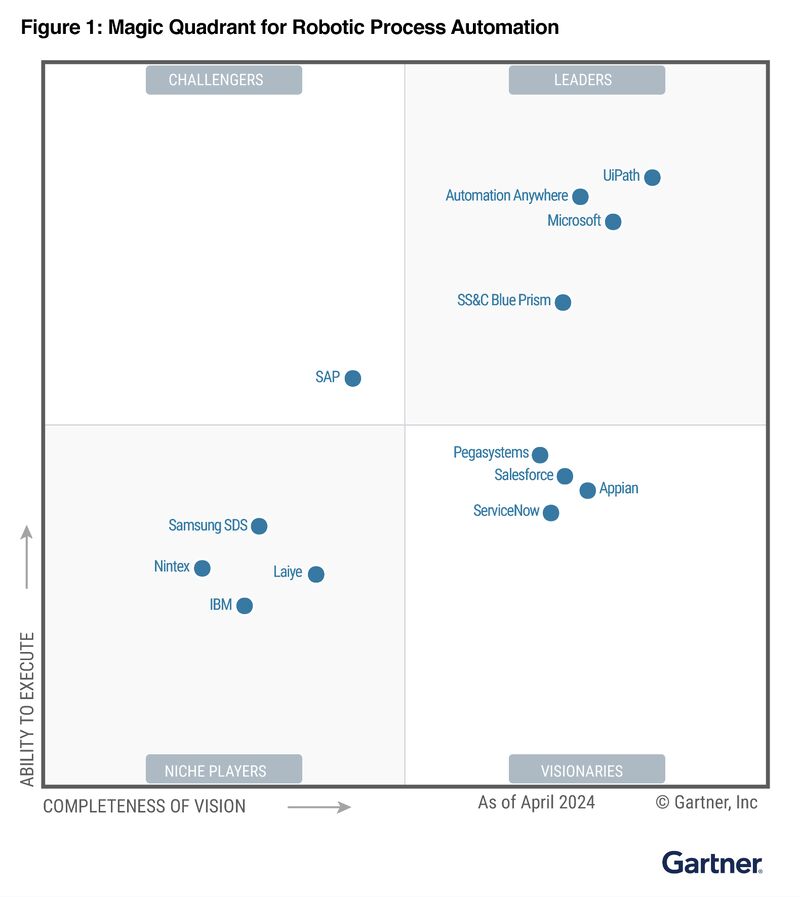
The Leaders quadrant remains largely unchanged, with the same four vendors maintaining their positions:
- UiPath
- Automation Anywhere (AA)
- Microsoft
- SS&C Blue Prism
This stability suggests that these vendors continue to demonstrate both a strong market presence and an innovative vision. However, it’s worth noting that Microsoft has made a notable upward move within the Leaders quadrant, indicating improved execution and/or vision compared to last year.
In a significant shift, SAP has moved from being a Visionary to the lone Challenger in this year’s quadrant. This change suggests that while SAP has strong execution capabilities, its vision for the future of RPA might not be as forward-looking as some of its competitors.
Notable Exits: Reshaping the Competitive Landscape
Several vendors have exited the Magic Quadrant this year, each for different reasons:
- NICE: Perhaps the most surprising exit, NICE is no longer considered an RPA vendor by Gartner. The report states that NICE “no longer considers itself an RPA vendor and does not actively market or sell an RPA product to its customers.”
- EdgeVerve Systems: Dropped due to not meeting the inclusion criteria for customer interest.
- Hyland: Also removed for not meeting criteria related to customer interest and revenue.
- Cyclone Robotics: While still supporting RPA, the company has shifted focus to AI-agent-based products.
These exits highlight the dynamic nature of the RPA market and the increasing importance of customer adoption and revenue growth for vendors to maintain their positions.
The AI Pivot: Reshaping the RPA Landscape
One of the most significant observations from this year’s report is the industry-wide pivot towards artificial intelligence. Gartner highlights three key trends that are shaping the RPA market:
1. AI at the Core of RPA Strategy
Vendors are positioning their platforms as essential tools in an AI-centric future. This includes focusing on:
- AI trust, risk, and security management (TRiSM)
- Enhanced AI skills and studios
- Development of both general-purpose and specialized large language models (LLMs)
2. Heavy Investment in Generative AI for Automation Development
RPA vendors are betting big on Generative AI to simplify automation development. Most are creating prompt-based development features that can translate natural language requests into automation workflows, making RPA more accessible to citizen developers.
3. Broader Orchestration and Automation Capabilities
RPA platforms are expanding beyond traditional robotic process automation to include technologies like:
- Intelligent document processing (IDP)
- Business process automation (BPA)
- Conversational AI
- Low-code application platforms (LCAP)
- Process mining
This AI-driven evolution raises questions about the long-term relevance of the RPA Magic Quadrant in its current form. As the lines between RPA and other automation technologies continue to blur, we may see a shift in how Gartner evaluates and categorizes these solutions.
The Rise of BOAT and Its Implications
Gartner’s pivot towards Business Optimization and Automation Technologies (BOAT) is another significant development. Gartner hints at the possibility of a new Magic Quadrant specifically for BOAT in the future. This shift reflects the growing convergence of various automation and optimization technologies and the need for a more holistic evaluation of these solutions.
The potential introduction of a BOAT Magic Quadrant could have implications for how organizations evaluate and select automation technologies. It may lead to a more comprehensive assessment of vendors’ capabilities across the entire automation spectrum, rather than focusing solely on RPA.
Microsoft’s Ascent: Potential and Challenges
Microsoft’s upward movement in the Leaders quadrant is noteworthy and suggests that the tech giant is making significant strides in the RPA space. With its extensive ecosystem and strong presence in enterprise software, Microsoft has the potential to eventually lead the pack.
However, the report also highlights some challenges that Microsoft faces, particularly around pricing. Gartner notes that “customers have reported additional costs that add up over time” and that some struggle to understand the different access levels provided by various enterprise licenses. This complexity in pricing could be a potential roadblock to Microsoft’s continued ascent in the RPA market.
Looking Ahead: The Future of RPA and Automation
As we analyze this year’s Magic Quadrant, it’s clear that the RPA market is at a crossroads. The rapid integration of AI capabilities, the expansion into broader automation technologies, and the potential shift towards BOAT all point to a future where traditional RPA may be just one component of a more comprehensive automation strategy.
For organizations evaluating RPA solutions, this evolving landscape presents both opportunities and challenges. While the core capabilities of RPA remain important, decision-makers must also consider:
- AI Integration: How well does the vendor incorporate AI into their RPA offering, and what tangible benefits does this bring?
- Broader Automation Capabilities: Does the platform offer a comprehensive suite of automation tools beyond just RPA?
- Flexibility and Scalability: Can the solution adapt to changing needs and grow with the organization?
- Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership: Are the pricing models clear, and do they offer good value over time?
Key Takeaways for Decision-Makers
As organizations navigate this evolving landscape, here are some key considerations:
- Evaluate AI Integration: Look beyond buzzwords and assess how well vendors integrate AI into their RPA offerings. Focus on tangible benefits and use cases that align with your organization’s needs.
- Consider the Broader Automation Ecosystem: While RPA remains important, evaluate vendors based on their ability to provide a comprehensive suite of automation tools. This may include process mining, IDP, and low-code development capabilities.
- Prioritize Flexibility and Scalability: Choose solutions that can adapt to your changing needs and grow with your organization. This includes support for both cloud and on-premises deployments, as well as the ability to handle increasing automation complexity.
- Scrutinize Pricing Models: With the increasing complexity of RPA and automation platforms, carefully evaluate pricing structures. Look for transparent models that offer good value over time and avoid hidden costs.
- Invest in Skills and Change Management: As RPA platforms become more sophisticated, invest in training and upskilling your workforce. This includes both technical skills for developers and business process knowledge for citizen developers.
- Stay Informed on BOAT Developments: Keep an eye on Gartner’s potential shift towards Business Optimization and Automation Technologies. This could significantly impact how you evaluate and select automation solutions in the future.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Automation
The 2024 Gartner Magic Quadrant for RPA reflects a market in transition. While the core capabilities of RPA remain important, the integration of AI and the expansion into broader automation technologies are reshaping the landscape. Organizations must adapt their strategies to embrace these changes while maintaining a focus on delivering tangible business value.
As we move forward, the lines between RPA and other automation technologies will continue to blur. The potential introduction of a BOAT Magic Quadrant signifies a new era in how we evaluate and implement automation solutions. Organizations should stay agile, keeping a close eye on these developments while focusing on solutions that can deliver tangible business value in both the short and long term.
Ultimately, success in this evolving landscape will depend on an organization’s ability to leverage automation technologies strategically, aligning them with broader digital transformation initiatives and business goals. By staying informed, adapting to change, and focusing on value creation, organizations can position themselves to thrive in the age of intelligent automation.